
Weather Station at Queens Botanical Garden |

Weather Station at Brooklyn Public Library - Brownsville Branch |
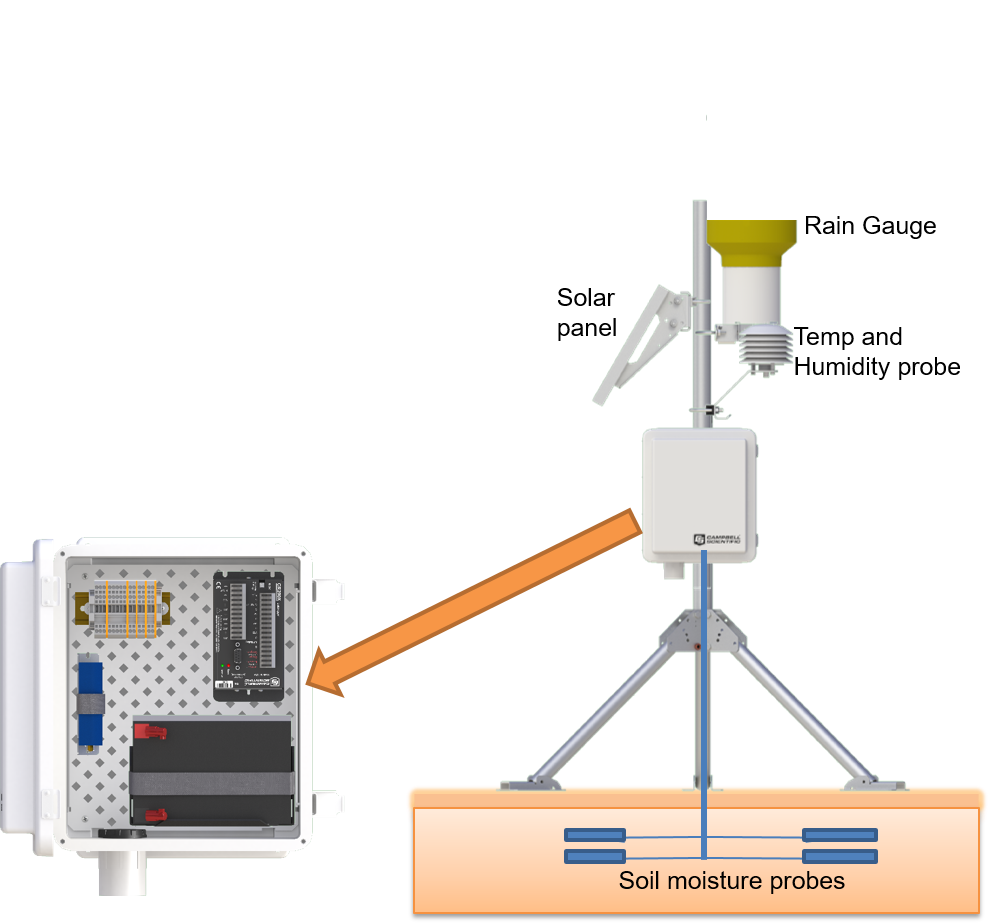
This figure depicts a schematic of a weather station, which includes various sensors such as temperature and humidity sensors, a rain gauge, and soil moisture sensors. The station also features a solar panel for power, a data logger for data storage, and a modem for wireless data transmission to the server. This setup enables the collection of precise and detailed weather and environmental data. |


